AUTO TRANSPORT
AN AUTONOMOUS DRIVING SYSTEM FOR CARS
COGNITIVE AUTO PILOT PERFORMS THE FOLLOWING TASKS
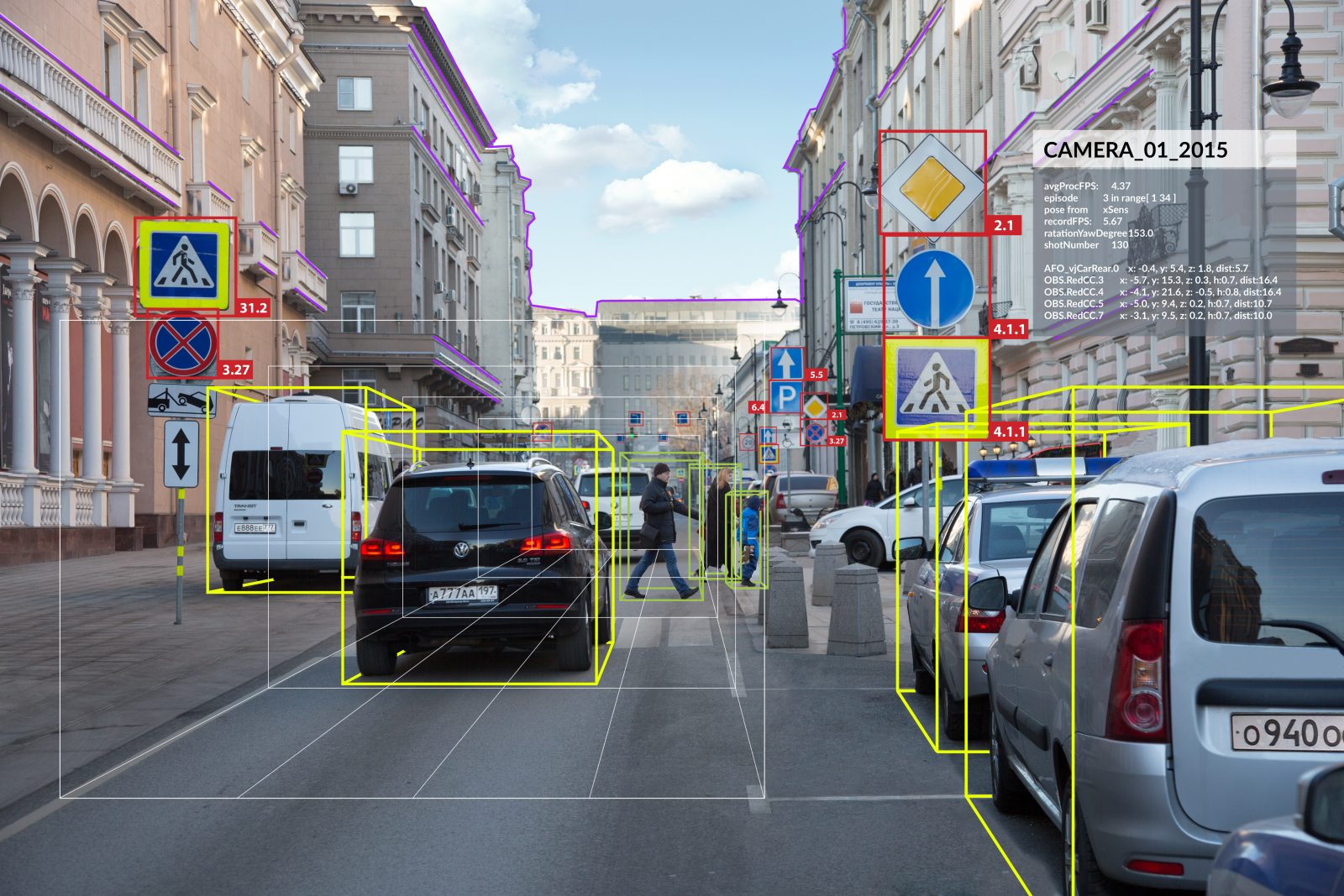
Cognitive Pilot’s approach to machine vision development allows for road scene recognition (including road edges, lane width, etc.) in real-world conditions (without road markings, with low-quality or non-existent surfacing, in challenging climatic and weather conditions, and so on). Cognitive Auto Pilot is capable of recognizing even partially obstructed objects that form part of the road scene, as well as problematic objects such as scooter riders, bikers, and cyclists.
The technology recognizes the roadway with or without mapping or other infrastructure elements. Its performance is not affected by weather, season, snow cover, asphalt or the lack of it, etc.
The “virtual tunnel” method is based on the principle that road scenes are inherently similar. The developers learned to identify the most inherent, fundamental properties of the roadway, be it a highway, a rural backroad, or a dirt road. This way, the system recognizes the roadway highly accurately and ensures the stable performance of the computer-vision algorithms based on this technology on various road configurations and in different conditions: at turns in either direction, on upward and downward slopes, at night, and in winter or other unfavorable climatic and weather conditions.
We have dubbed the developed technology “virtual tunnel” because this is what the sequence of rectangular interest zones looks like in perspective.
This technology can serve as a basis for high-performance ADS systems of level 3–5, which ensure the reliable detection of a roadway of any shape and geometry, including in bad weather and harsh climatic conditions.

With CLLDF technology, combined data fed into the computing unit of a computer vision model from different sensors (video cameras, radar and lidar units, etc.) is put to the best possible use.
The architecture of Cognitive Low-Level Data Fusion allows detailed information about the road scene to be received from several sensors. So if, for example, a radar signal detects an obstacle ahead but the video camera cannot see it clearly due to sun dazzle, the AI categorizes the situation as problematic and either requests more detailed information from the camera or makes a decision based on radar data.

Intuition is often the key decision-making factor for human drivers. As you may know, cognitive psychology explains intuitive thinking as the human ability to process complex information inadvertently and unconsciously. In the course of intuitive cognition, people do not realize all the factors that have affected their conclusion. It is the conclusion itself that we realize with the most extreme clarity.
The technology employs a range of solutions, including the detection and dynamic analysis of small-scale elements of the road scene and objects on the road. For instance, it is possible to predict the course of the car ahead by observing the changes in the position of its tail lights or side mirror.